Above All Else Show the Data
Best Practices in Data Visualization
University of Houston
2023-05-24
What is the point of data visualization?
What pattern do you see?
Data graphics visually display measured quantities by means of combined use of points, line, a coordinate system, numbers, symbols, words, shading and color (Tufte 2015).
But not all graphics are created equal
Agenda
- Principles of Graphical Excellence
- Data distortions
- Data-ink
- Identify graphic crimes
- The importance of color
- Socially responsible visualizations
- Resources

Principles of Graphical Excellence
Excellence in statistical graphics consist of complex ideas communicated with clarity, precision, and efficiency (Tufte 2015, pg 14)
Graphics should…
- show the data
- induce viewer to think about the substance and not methodology, design, or technology
- avoid distorting the data
- present many numbers in a small space
- make large data sets coherent
- compare different pieces of the data
- reveal the data at several levels of detail
- display a clear purpose
Data Maps: Death Rates from Cancer, Female


Data Maps: Death Rates from Cancer, Male


Graphical Integrity: Proportionality
The representation of numbers, as physically measured on the surface of the graphic itself, should be directly proportional to the numerical quantities (pg.56)
Different people see the same areas differently and perceptions change with experience and context
Tables sometimes outperform graphics in clarity, but only for small data sets of 20 numbers or less
Fuel Economy Standards

Fuel Economy Standards

\[ \frac{27.5-18.0}{18.0} \times 100=53\% \]
\[ \frac{5.3-0.6}{0.6} \times 100=783\% \]
Graphical Integrity: Labeling
Clear, detailed, and thorough labeling should be used to defeat distortion and ambiguity
Write out explanations of the data and label important events
Includes labeling the coordinate system and providing an informative title
Fuel Economy Clarified

Data-Ink
A large share of ink on a graphic should present data-information
Data ink is the non-erasable core of a graphic arranged in response to variation in the numbers represented
Every bit of ink on a graphic requires a reason - and that reason is to present new information
![]()
Erase non-data-ink
What elements of this chart are not data-ink?

Erase non-data-ink
The grid lines!

Erase non-data-ink

Erase non-data-ink

Erase non-data-ink

Pie Charts
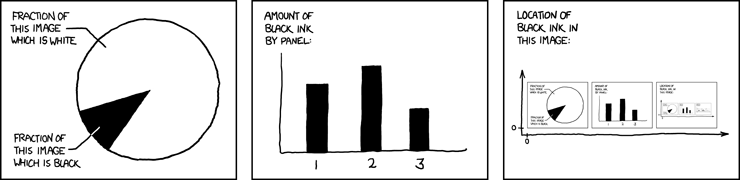
The Pie Proof1
What is the pattern here?
Can you see the pattern now?
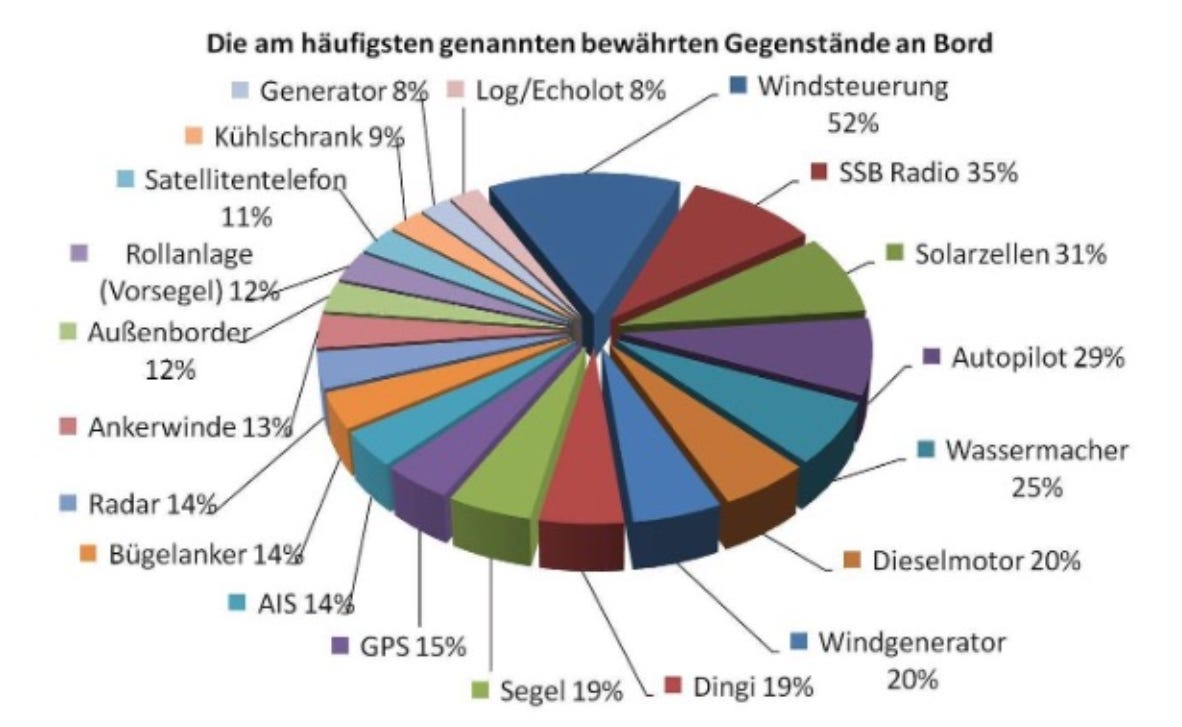
Pies are for eating, not charting
What’s wrong with this visualization?

What’s wrong with this visualization?

What’s wrong with this visualization?

COLORS!
Colors are an important aesthetic
All data visualizations use color, depending on how you define black and white
Three ways to use colors
Qualitative colors show category
Sequential colors show order, rank, or numeric values
Diverging colors show values that move around a zero mark
Qualitative1

Sequential

Diverging

Color Brewer

Improving graphics with/out color1
Move color mapping to bar height

Improving graphics with/out color
Move color mapping to bar height and position

Color consistency

Color to highlight relationships in context

Color ramps must match psychology

Accessible colors

Equity Awareness

Equity awareness in data visualization1
Data analysts should think intentionally about how we can learn from and speak to audiences that reflect the diversity of the people and communities we focus
Systemic discrimination is and can be generated by how we use and misuse data
If I were one of the data points on this visualization, would I feel offended? - Kim Bui

Demonstrating empathy
Put people first: data shown reflect the lives and experiences of real people
Use personal connections to help readers and users better connect with the material: pair charts with personal stories
Create a platform for engagement: interactive graphics allow users to find themselves in the data
Consider how framing an issue can create a biased emotional response
If the underlying data is biased, graphics can amplify bias and the harm that bias generates
Put people first

Put people first

Language and racial equity awareness

Ordering data purposefully

Colors and equity awareness

Colors and equity awareness

Conclusion
Remember the Principles of Graphical Excellence: clarity, precision, and efficiency
Avoid data distortion through Graphical Integrity
Maximize data-ink ratio
Have a clear purpose for your graphics: what do you want to communicate?
Do no harm: be aware how your data graphics perpetuate bias or systemic discrimination
Above All Else Show the Data!
Additional Resources
Data-to-Viz: Find the Right Viz

WTF Viz: Examples of what not to do

Atkinson Hyperlegible Font
Free downloadable font for low-vision readers by the Braille Institute used throughout this presentation.

Contact
Jorge Martinez
University of Houston
Director of Research and Reporting
Enrollment Services

Best Practices in Data Visualization